MEASURED RUNNING PARAMETERS
- Engine speed
- TC speed
- Fuel rack position
- Charge air pressure / temperature
- Pressure difference over CA cooler
- Pressure difference over cylinders
- Exhaust gas temperatures
ENGINE SPEED:
- Measured by cam shaft wheel, or flywheel.
- Unstably engine speed can be caused by wrong governor settings, worn/jamming regulating mechanism.
- Engine speed controls pre.lub pump start and stop, pre.heating start and stop, by-pass valve function.
- Alarm / safety blockings.
- Safety functions; clutch opening, over speed.
TURBO CHARGER SPEED:
- An important factor to follow since the turbo speed gives an indication when the nozzle ring gets dirty. I.e. the turbo speed increases slightly.
FUEL RACK POSITION
- Indicates amount of sprayed fuel oil (engine load).
- Increased fuel rack index (same load) can be result of worn pump (bigger internal leakages) or change on fuel quality, lower heat value.
IGNITION QUALITY PARAMETERS:
- Energy
- Viscosity
- Maximum firing pressure.
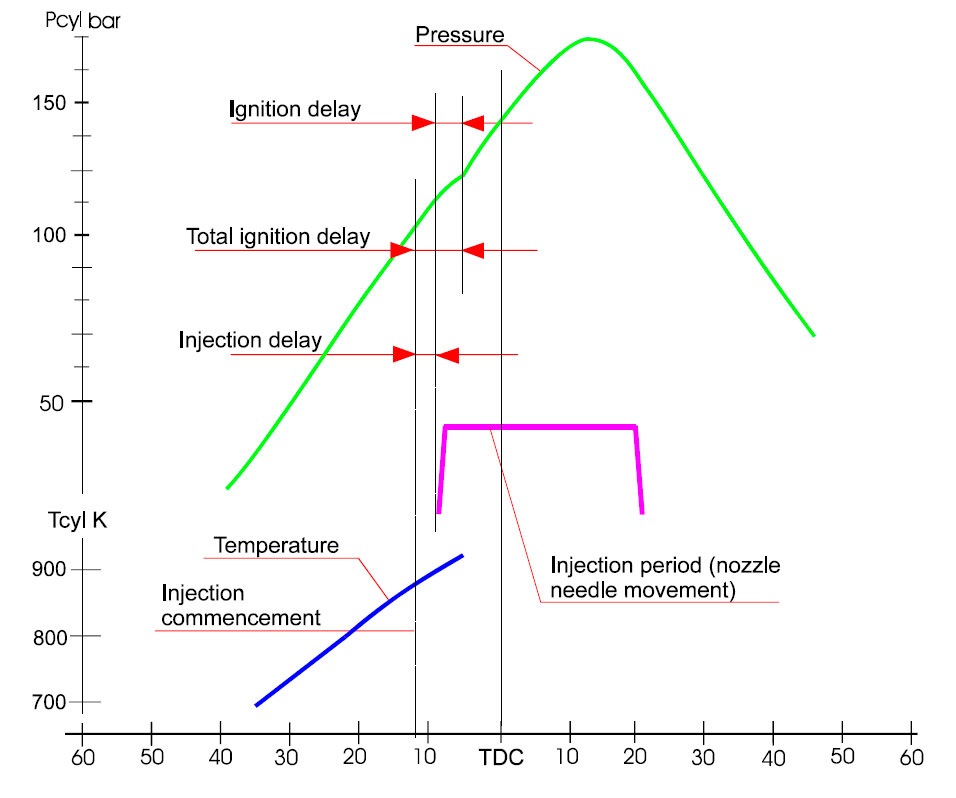
- Injection delay
- Ignition delay
ENERGY COMPARISON
- The injection pump is a volumetric pump
- The higher the density the more energy it contains per volume unit
- The density difference between HFO and MDO is larger than the difference in net calorific value
VISCOSITY COMPARISON
- The viscosity of MDO is lower than the viscosity of HFO (even HFO is heated)
- Lower viscosity fuels result in more internal leakage in the injection pump from the high pressure side to low pressure side.
- Internal leakage has to be compensated by giving more fuel rack
MAXIMUM FIRING PRESSURE
- Dependent on the charge air pressure
- To achieve proper combustion, the firing pressure has to be high and thus also the charge air pressure
- Timing of the fuel pump
- INJECTION DELAY is the time it takes to build up a pressure higher than the opening pressure of the nozzle.
- Normally 4...5 ° of crank angle
- The delay is comparable to the condition of injection equipment
- IGNITION DELAY is the time gap between the commencement of injection and the commencement of ignition.
- Dependent on the fuel quality
- Compression temperature has a big influence on the ignition delay
- Compression temperature is not high enough for the fuel to ignite longer ignition delay
HIGHER PEAK PRESSURES AND HIGHER EXHAUST GAS TEMPERATURES.
- Normally 1...2 ° of crank angle.
- Too early timing of injection
- Higher peak pressure
EXHAUST GAS TEMPERATURE AFTER CYLINDER
- Measured individually after each cylinder
- Each cylinder has two measuring points.
- The average temperature of all exhaust temperature sensors is approximately 100 °C lower than the exhaust gas temperature before the turbine.
- Maximum allowed difference between valves in one cylinder.
- Maximum allowed difference of one cylinders average from the average of the all cylinders , alarm.
- In normal operation the average temperature Cylinder temperature deviation can be up to 30 - 40 °C.
- Engine is (depending of installation) provided with a safety slow down arrangement if the temperature difference is too big
- A 10 °C increase in ambient temperature will result approximately 15 °C increase in exhaust gas temperature
EXHAUST GAS TEMPERATURE AFTER TURBOCHARGER
- Indicates the kinetic energy of the exhaust gases that are running the turbine
- Indicates the condition of the turbo, i.e. scavenging of the engine
- If a de-Nox catalysator is installed the temperature has to exceed certain level to ensure the function of the catalysator
PRESSURE DIFFERENCE OVER THE CYLINDERS:
- Measuring the pressure difference between charge air manifold and exhaust gas manifold. gives an indication of how well the scavenging works.
- Depends on the turbocharger, therefore values below should be considered as allusive
- The bigger the Dp is the better scavenging.
- Is normal value with 100% load varies depending of installation once the value has been dropped down, it is an indication that something is wrong with the engine -e.g. dirty nozzle ring & turbine
DIRTY CHARGE AIR COOLER:
- Indicated by the increase of the pressure difference over the cooler, remember that the cleaning of the cooler is aggravated with the dirtiness of the cooler.
CONSEQUENCES:
- Less fresh air to cylinders
- Higher exhaust gas temperatures
- Improper combustion
- Low peak pressures
- More deposits to nozzle ring
- Increased SFOC
- Increased SLOC
- Higher fuel rack reading at the same load
CONDENSE WATER IN CHARGE AIR:
- Condense water that is condensing in the cooler has to be drained out
- Causes wear in the pistons, piston rings and cylinder heads
- Will cause inlet seat ring problems
- The amount of condensed water may be reduced by increasing the charge
- Air temperature, but the maximum temp must not be exceeded which is 55 ° C
- Increases thermal loading of the engine
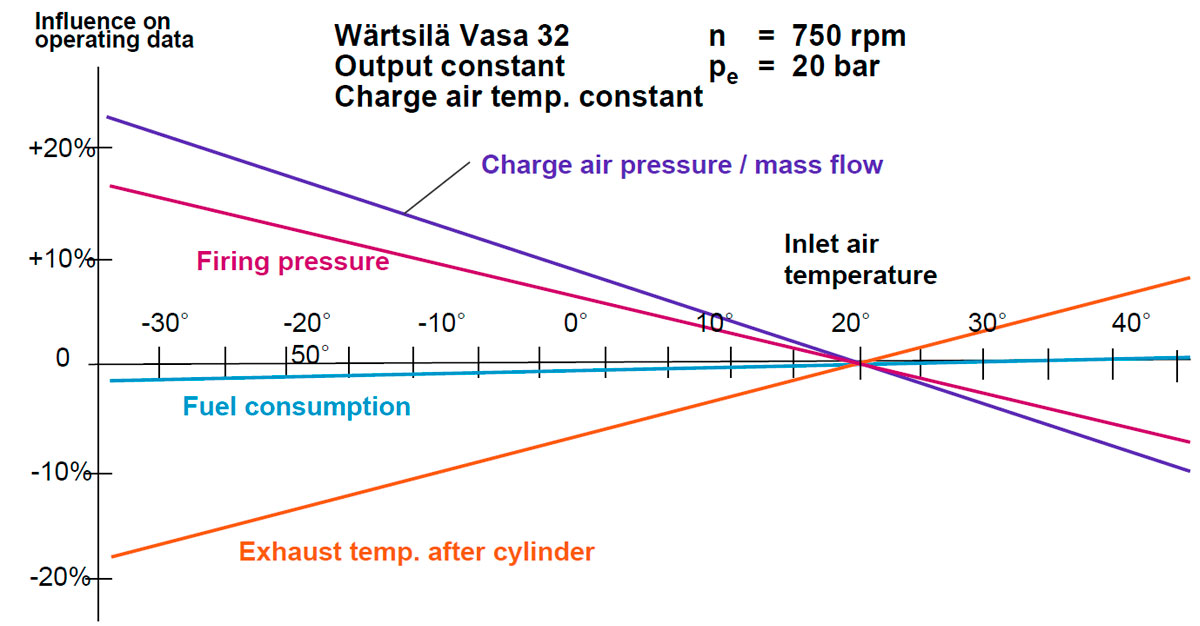
DIRTY NOZZLE RING:
- Indicated by;
- Slightly higher turbine speed
- Higher receiver temperature
- Decreased pressure difference over the cylinders
2. POSSIBLE CONSEQUENCES;
- Remainder pressure in the cylinders increase
- less fresh air to cylinders
- worse scavenging
- delayed combustion
- more deposit accumulations
- higher exhaust gas temperatures
- increased thermal load
- increased risk of engine failure
- piston seizure
- hot corrosion
- increased fuel consumption.
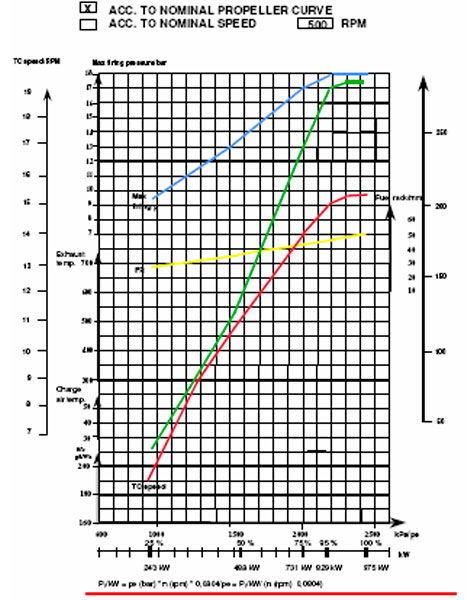
LOW PEAK PRESSURES-HIGH EXHAUST GAS TEMPERATURES:
- Obvious reason:
- DELAYED COMBUSTION
- Dirty air cooler
- dirty nozzle ring(s)
- injection nozzles in bad condition
- worn injection pumps
- a long injection delay
- bad fuel
- high CCAI value poor ignition properties
- high water content
- high exhaust gas temp
HIGH EXHAUST GAS TEMPERATURES:
- Obvious reason
- Injection valves in bad condition
- dirty nozzle ring
- dirty air cooler
- Low fuel viscosity
- worn injection pumps
- bad fuel
- burned valves or seats
HIGH FUEL RACK READING COMPARED TO LOAD
- Worn injection pumps
- more internal leakage
- too low viscosity of the fuel
- more internal leakage
- low heat value of the fuel
- high water content
- dirty fuel filter
- too low fuel pressure
- big fuel leakage
Литература
www.wartsila.com

